Marine Biodiversity
and Climate Change
Research Lead – Dr Nova Mieszkowska
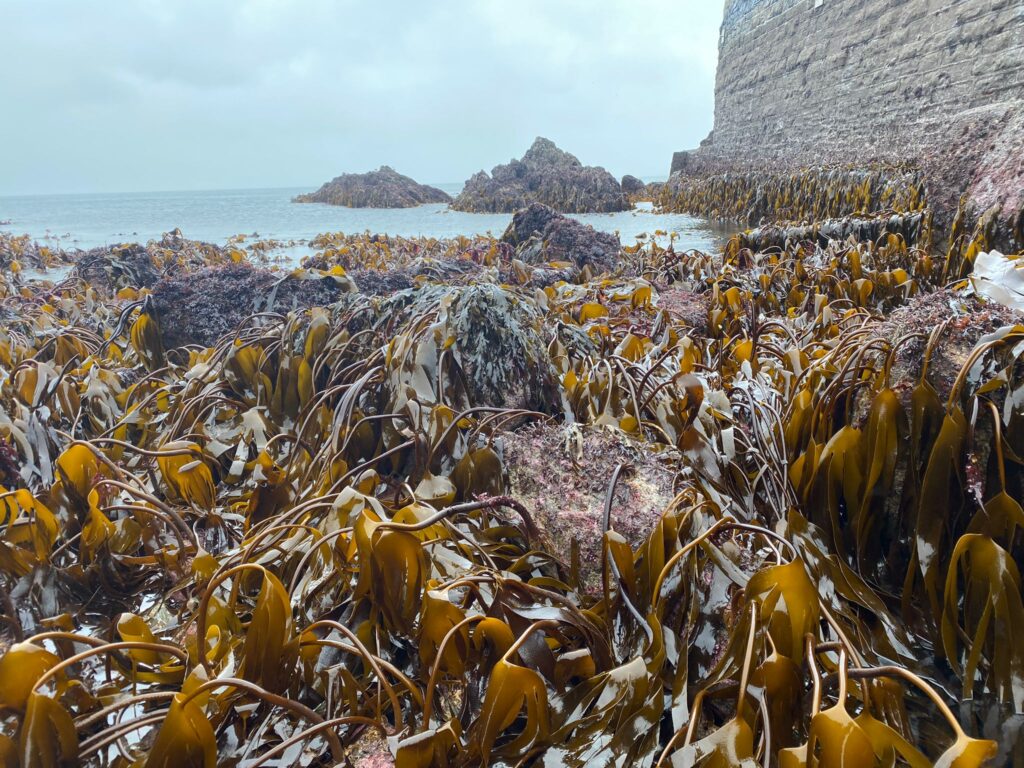
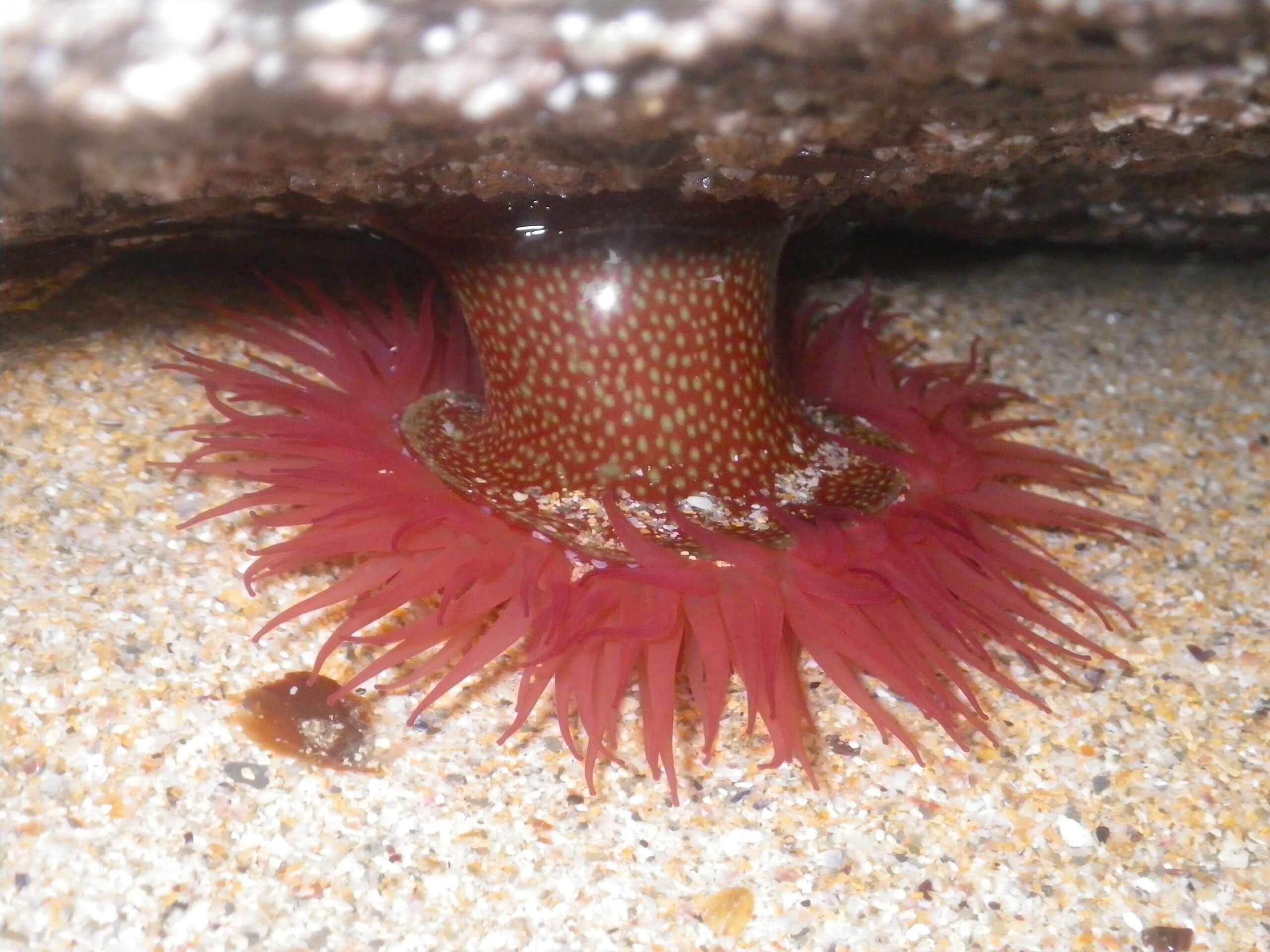
The MarClim project is the most spatio-temporally extensive time-series for intertidal systems globally. MarClim surveys track the abundance and distribution of 87 species of invertebrates and macroalgae at 100 sites around the UK Regional Seas and northern France on an annual basis. The project has recorded some of the fastest distributional shifts in leading and trailing range edges of species in any natural system. MarClim is one of the MBA long-term time-series which span over half a century.
This work has been extended to other temperate regions around the world including Europe, Australia, and New Zealand. We are interested in identifying the biological mechanisms and changes in gene expression occuring in invertebrates and macroalgae that underpin the macroecological responses to climate warming and ocean acidification. To develop this line of research the genome of every MarClim species is being sequenced as part of the MBA’s role in the Darwin Tree of Life Project. Current research using combined laboratory and field experiments is investigating how increasing temperatures and ocean acidification are altering reproductive cycles, impacting performance and recruitment, and identifying the effects of climate change on invasive capabilities of non-natives.

Our Research Impacts
Assessing native intertidal biodiversity
MarClim data have been developed as Good Environmental Status indicators for the UK Marine Strategy. These indicators have been designed to assess the ‘maintain native intertidal biodiversity’ target and developed as the UK Intertidal Community Temperature Index (CTI), a measure of the status of a community in terms of its species composition of coldwater (boreal) and warmwater (lusitanian) species. These indicators are used to assess progress against the following target, which is set in the UK Marine Strategy Part 1: Maintain native intertidal biodiversity (HM Government, 2012).
Protecting a Special Area of Conservation
A survey of biological indicators of ecological effects of Tributyltin (TBT) release sometime in 2015 to 2016 in the Yealm Estuary, south Devon by the Marine Biological Association of the UK (MBA) was commissioned by the Environment Agency (EA) on 28th November 2022. The report was used in subsequent legal proceedings which led to a fine for multi-national owned International Paint Ltd. for allowing the banned chemical to enter the Site of Special Scientific Interest designated Yealm estuary in Devon.
Key Publications
Latest Projects
The Marine Biodiversity and Climate Change Project

MarClim has the most spatio-temporally extensive time-series of rocky intertidal systems globally. Eighty seven species of invertebrate and macroalgae of boreal, Lusitanian, and invasive origins are surveyed at one hundred sites around the coastlines of the UK and northern France and surveyed every year. MarClim has shown some of the fastest biogeographic range shifts in response to climate change in any natural system. The data are used by Natural Resources Wales and Natural England and form part of Condition Assessments for MPAs.
The Darwin Tree of Life Project

The Darwin Tree of Life project aims to sequence the genomes of 70,000 species of eukaryotic organisms in Britain and Ireland. It is a collaboration between biodiversity, genomics and analysis partners that is transforming the way we do biology, conservation, and biotechnology. The Darwin Tree of Life Project is one of several initiatives across the globe working towards the ultimate goal of sequencing all complex life on Earth, in a venture known as the Earth BioGenome Project. The Marine Biological Association is the lead Genome Acquisition Laboratory for marine species.
FutureMARES

FutureMARES is an EU-funded research project examining the relations between climate change, marine biodiversity, and ecosystem services. The project’s activities are designed around two Nature-based Solutions (NBS) and one Nature-inclusive Harvesting (NIH). We are conducting our research and cooperating with marine organisations and the public in five regions across the globe. Our goal is to provide science-based policy advice on how best to use NBS/NIH to protect future biodiversity and ecosystem services in a future climate. The MarClim time-series is one of the biological time-series being used in the project.
Latest News
Our Team
Dr Nova Mieszkowska
Senior Research Fellow
Dr Nova Mieszkowska
Senior Research Fellow
My international research programme focuses on species and ecosystem-level responses to environmental change and multiple stressors in the marine environment, embedding small-scale, process-oriented experimental studies within larger scale macroecological investigations. This approach focuses on individual organisms via experimental physiological ecology and ecological genomics, integrating to the population level with long-term time-series data collection, analysis and modelling to identify mechanisms of species response. I am the principal investigator for the Marine Biodiversity & Climate Change Project (MarClim), which has the most spatio-temporally extensive time-series of rocky intertidal systems globally. MarClim has shown some of the fastest biogeographic range shifts in response to climate change in any natural system. I have also been involved with the Intergovernmental Panel for Climate Change (IPCC) in various capacities for more than a decade. My science-policy knowledge exchange work includes provision of field survey and monitoring data and assessments of ecosystem status, contributions to national and international policy drivers, authorship on national reports including the Marine Climate Change Impacts Partnership Annual Report Cards, and presenting to UK government and EU bodies. I have developed indicators of Good Environmental Status for implementation of the Marine Strategy Framework Directive in intertidal and subtidal habitats around the UK.





